Plots Visual
Plot y versus x as lines and/or markers.
Call signatures:
- Stem and leaf plots are data dense visualizations that organize large amounts of micro-level numeric data to form larger macro-level visual distributions. These plots can be extended with font.
- Created by Tom Breloff (@tbreloff) Maintained by the JuliaPlots members. Plots is a plotting API and toolset. My goals with the package are: Powerful. Do more with less. Complex visualizations become easy. Stop reading so much documentation. Commands should 'just work'. Less code means fewer mistakes and more.
- Correlation plots can be used to quickly find insights. It is used to investigate the dependence between multiple variables at the same time and to highlight the most correlated variables in a data table. In this visual, correlation coefficients are colored according to the value.
Try these plot ideas to get your brain a’storming. Some are realistic. Others are just ludicrous. Some have been done before. The point is for you to tell the story differently. Ask yourself why when reading these. A world wherein employees work nonstop with no vacation—a riot ensues.
The coordinates of the points or line nodes are given by x, y.
The optional parameter fmt is a convenient way for defining basicformatting like color, marker and linestyle. It's a shortcut stringnotation described in the Notes section below.
You can use Line2D properties as keyword arguments for morecontrol on the appearance. Line properties and fmt can be mixed.The following two calls yield identical results:
When conflicting with fmt, keyword arguments take precedence.
Plotting labelled data
There's a convenient way for plotting objects with labelled data (i.e.data that can be accessed by index obj['y']). Instead of givingthe data in x and y, you can provide the object in the dataparameter and just give the labels for x and y:
All indexable objects are supported. This could e.g. be a dict, apandas.DataFame or a structured numpy array.
Plotting multiple sets of data
There are various ways to plot multiple sets of data.
The most straight forward way is just to call
plotmultiple times.Example:Alternatively, if your data is already a 2d array, you can pass itdirectly to x, y. A separate data set will be drawn for everycolumn.
Example: an array
awhere the first column represents the xvalues and the other columns are the y columns:The third way is to specify multiple sets of [x], y, [fmt]groups:
In this case, any additional keyword argument applies to alldatasets. Also this syntax cannot be combined with the dataparameter.
By default, each line is assigned a different style specified by a'style cycle'. The fmt and line property parameters are onlynecessary if you want explicit deviations from these defaults.Alternatively, you can also change the style cycle usingrcParams['axes.prop_cycle'] (default: cycler('color', ['#1f77b4', '#ff7f0e', '#2ca02c', '#d62728', '#9467bd', '#8c564b', '#e377c2', '#7f7f7f', '#bcbd22', '#17becf'])).
| Parameters: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Returns: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Parameters: |
|
See also
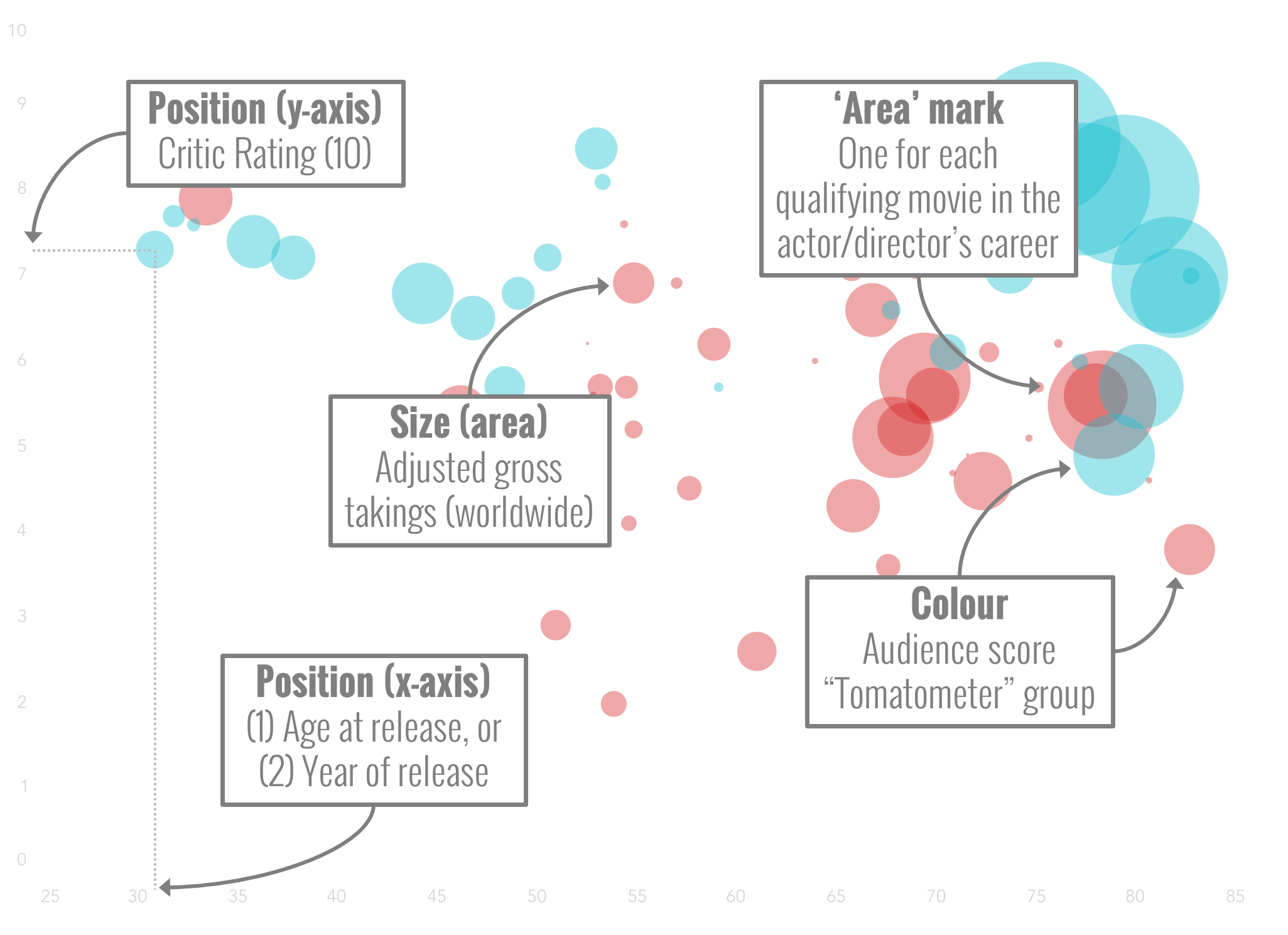
scatter- XY scatter plot with markers of varying size and/or color ( sometimes also called bubble chart).
Notes
Format Strings
A format string consists of a part for color, marker and line:
Each of them is optional. If not provided, the value from the stylecycle is used. Exception: If line is given, but no marker,the data will be a line without markers.
Other combinations such as [color][marker][line] are alsosupported, but note that their parsing may be ambiguous.
Markers
| character | description |
|---|---|
'.' | point marker |
',' | pixel marker |
'o' | circle marker |
'v' | triangle_down marker |
'^' | triangle_up marker |
'<' | triangle_left marker |
'>' | triangle_right marker |
'1' | tri_down marker |
'2' | tri_up marker |
'3' | tri_left marker |
'4' | tri_right marker |
's' | square marker |
'p' | pentagon marker |
'*' | star marker |
'h' | hexagon1 marker |
'H' | hexagon2 marker |
'+' | plus marker |
'x' | x marker |
'D' | diamond marker |
'd' | thin_diamond marker |
' ' | vline marker |
'_' | hline marker |
Line Styles
| character | description |
|---|---|
'-' | solid line style |
'--' | dashed line style |
'-.' | dash-dot line style |
':' | dotted line style |
Example format strings:
Colors
The supported color abbreviations are the single letter codes
| character | color |
|---|---|
'b' | blue |
'g' | green |
'r' | red |
'c' | cyan |
'm' | magenta |
'y' | yellow |
'k' | black |
'w' | white |
Comparing Dot Plots Visually
and the 'CN' colors that index into the default property cycle.
Plot Visual
If the color is the only part of the format string, you canadditionally use any matplotlib.colors spec, e.g. full names('green') or hex strings ('#008000').